zset的数据结构
在redis中有一个有序列表,它的底层是由压缩列表或跳表组成。我们看下对应的数据结构
压缩链表:

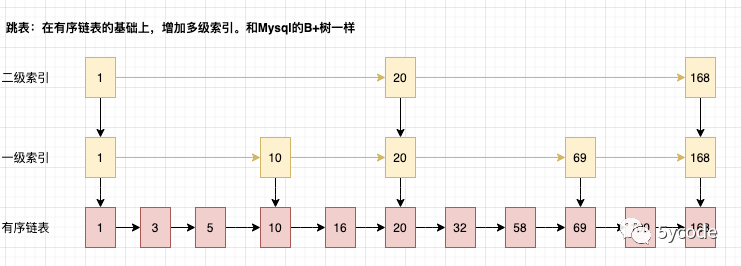
跳表:
下载下来4.0的源码 https://download.redis.io/releases/redis-4.0.0.tar.gz
对应的源码:
src/server.h
# 最大层级
#define ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL 32 /* Should be enough for 2^32 elements */
# 表示上一层级是下一层级的1/4,相当于是一棵四叉树
#define ZSKIPLIST_P 0.25 /* Skiplist P = 1/4 */
typedef struct zset {
dict *dict;
zskiplist *zsl;
} zset;
typedef struct zskiplist {
// 头节点,尾节点
struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail;
//长度
unsigned long length;
//当前索引的层数
int level;
} zskiplist;
typedef struct zskiplistNode {
// 动态字符串,member 对象
sds ele;
// 分值表示顺序
double score;
// 后退指针
struct zskiplistNode *backward;
//索引层
struct zskiplistLevel {
// 前进指针指向node
struct zskiplistNode *forward;
// 这个层跨越的节点数量
unsigned int span;
} level[];
} zskiplistNode;
#src/t_zset源码
int zslRandomLevel(void) {
int level = 1;
while ((random()&0xFFFF) < (ZSKIPLIST_P * 0xFFFF))
level += 1;
return (level<ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL) ? level : ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL;
}
我们看下zadd的源码:
/* This generic command implements both ZADD and ZINCRBY. */
void zaddGenericCommand(client *c, int flags) {
static char *nanerr = "resulting score is not a number (NaN)";
robj *key = c->argv[1];
robj *zobj;
sds ele;
double score = 0, *scores = NULL;
int j, elements;
int scoreidx = 0;
/* The following vars are used in order to track what the command actually
* did during the execution, to reply to the client and to trigger the
* notification of keyspace change. */
int added = 0; /* Number of new elements added. */
int updated = 0; /* Number of elements with updated score. */
int processed = 0; /* Number of elements processed, may remain zero with
options like XX. */
/* Parse options. At the end 'scoreidx' is set to the argument position
* of the score of the first score-element pair. */
# 解析参数
scoreidx = 2;
while(scoreidx < c->argc) {
char *opt = c->argv[scoreidx]->ptr;
if (!strcasecmp(opt,"nx")) flags |= ZADD_NX;
else if (!strcasecmp(opt,"xx")) flags |= ZADD_XX;
else if (!strcasecmp(opt,"ch")) flags |= ZADD_CH;
else if (!strcasecmp(opt,"incr")) flags |= ZADD_INCR;
else break;
scoreidx++;
}
#参数转换
/* Turn options into simple to check vars. */
int incr = (flags & ZADD_INCR) != 0;
int nx = (flags & ZADD_NX) != 0;
int xx = (flags & ZADD_XX) != 0;
int ch = (flags & ZADD_CH) != 0;
/* After the options, we expect to have an even number of args, since
* we expect any number of score-element pairs. */
# 参数必须成对
elements = c->argc-scoreidx;
if (elements % 2 || !elements) {
addReply(c,shared.syntaxerr);
return;
}
elements /= 2; /* Now this holds the number of score-element pairs. */
/* Check for incompatible options. */
if (nx && xx) {
addReplyError(c,
"XX and NX options at the same time are not compatible");
return;
}
if (incr && elements > 1) {
addReplyError(c,
"INCR option supports a single increment-element pair");
return;
}
/* Start parsing all the scores, we need to emit any syntax error
* before executing additions to the sorted set, as the command should
* either execute fully or nothing at all. */
# 遍历所有要添加的元素,score必须是数字
scores = zmalloc(sizeof(double)*elements);
for (j = 0; j < elements; j++) {
if (getDoubleFromObjectOrReply(c,c->argv[scoreidx+j*2],&scores[j],NULL)
!= C_OK) goto cleanup;
}
/* Lookup the key and create the sorted set if does not exist. */
# zset不存在就加锁创建
zobj = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,key);
if (zobj == NULL) {
if (xx) goto reply_to_client; /* No key + XX option: nothing to do. */
#选择存储结构
if (server.zset_max_ziplist_entries == 0 ||
server.zset_max_ziplist_value < sdslen(c->argv[scoreidx+1]->ptr))
{
# 跳表
zobj = createZsetObject();
} else {
# 压缩列表
zobj = createZsetZiplistObject();
}
# 将创建好的数据结构添加到db中
dbAdd(c->db,key,zobj);
} else {
if (zobj->type != OBJ_ZSET) {
addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr);
goto cleanup;
}
}
for (j = 0; j < elements; j++) {
double newscore;
score = scores[j];
int retflags = flags;
# 从参数中获取元素member
# ZADD key score member [[score member] [score member] ...]
ele = c->argv[scoreidx+1+j*2]->ptr;
# 添加逻辑具体看zsetAdd
int retval = zsetAdd(zobj, score, ele, &retflags, &newscore);
# 添加失败就清空
if (retval == 0) {
addReplyError(c,nanerr);
goto cleanup;
}
if (retflags & ZADD_ADDED) added++;
if (retflags & ZADD_UPDATED) updated++;
if (!(retflags & ZADD_NOP)) processed++;
score = newscore;
}
server.dirty += (added+updated);
reply_to_client:
if (incr) { /* ZINCRBY or INCR option. */
if (processed)
addReplyDouble(c,score);
else
addReply(c,shared.nullbulk);
} else { /* ZADD. */
addReplyLongLong(c,ch ? added+updated : added);
}
cleanup:
zfree(scores);
if (added || updated) {
signalModifiedKey(c->db,key);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_ZSET,
incr ? "zincr" : "zadd", key, c->db->id);
}
}
void zaddCommand(client *c) {
zaddGenericCommand(c,ZADD_NONE);
}
void zincrbyCommand(client *c) {
zaddGenericCommand(c,ZADD_INCR);
}
int zsetAdd(robj *zobj, double score, sds ele, int *flags, double *newscore) {
if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
if ((eptr = zzlFind(zobj->ptr,ele,&curscore)) != NULL) {
# 存在的时候,删除并替换
if (score != curscore) {
zobj->ptr = zzlDelete(zobj->ptr,eptr);
zobj->ptr = zzlInsert(zobj->ptr,ele,score);
*flags |= ZADD_UPDATED;
}
return 1;
} else if (!xx) {
/* Optimize: check if the element is too large or the list
* becomes too long *before* executing zzlInsert. */
zobj->ptr = zzlInsert(zobj->ptr,ele,score);
#在满足zset_max_ziplist_entries 和zset_max_ziplist_value的时候,转化成跳表
if (zzlLength(zobj->ptr) > server.zset_max_ziplist_entries)
zsetConvert(zobj,OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST);
if (sdslen(ele) > server.zset_max_ziplist_value)
zsetConvert(zobj,OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST);
if (newscore) *newscore = score;
*flags |= ZADD_ADDED;
return 1;
} else {
*flags |= ZADD_NOP;
return 1;
}
} else if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) {
zset *zs = zobj->ptr;
zskiplistNode *znode;
dictEntry *de;
# 存在的时候,删除并替换
de = dictFind(zs->dict,ele);
if (de != NULL) {
if (score != curscore) {
zskiplistNode *node;
serverAssert(zslDelete(zs->zsl,curscore,ele,&node));
znode = zslInsert(zs->zsl,score,node->ele);
node->ele = NULL;
zslFreeNode(node);
/* Note that we did not removed the original element from
* the hash table representing the sorted set, so we just
* update the score. */
dictGetVal(de) = &znode->score; /* Update score ptr. */
*flags |= ZADD_UPDATED;
}
return 1;
} else if (!xx) {
# 将元素转为sds
ele = sdsdup(ele);
znode = zslInsert(zs->zsl,score,ele);
serverAssert(dictAdd(zs->dict,ele,&znode->score) == DICT_OK);
*flags |= ZADD_ADDED;
if (newscore) *newscore = score;
return 1;
} else {
*flags |= ZADD_NOP;
return 1;
}
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown sorted set encoding");
}
return 0; /* Never reached. */
}
在redis的官方文档中 https://raw.githubusercontent.com/redis/redis/4.0/redis.conf 有个配置参数:
# Similarly to hashes and lists, sorted sets are also specially encoded in
# order to save a lot of space. This encoding is only used when the length and
# elements of a sorted set are below the following limits:
zset-max-ziplist-entries 128
zset-max-ziplist-value 64
简单的梳理下流程:
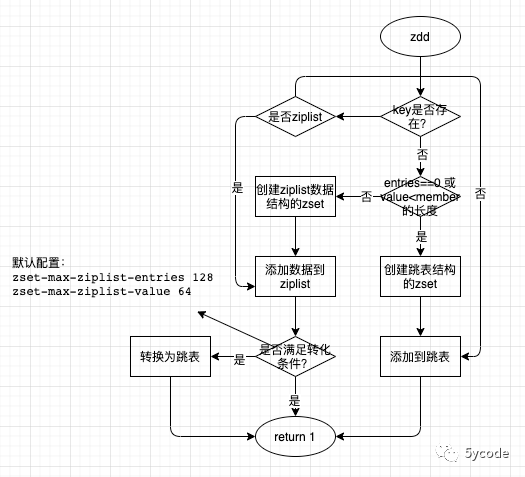
-
最开始数据量少,选择的压缩列表的数据结构
-
当所保存的元素超过了zset-max-ziplist-entries对应的值(默认128)转换为跳表;
-
当添加元素的member的长度大于zset-max-ziplist-value对应的值(默认64)转换为跳表
通过以上资料,我们可以推断下:
-
在小数据量的时候,压缩列表的性能不会比跳表差太多;
-
通过数据结构的对比,压缩列表在有序性上的性能损耗相对较大,插入数据需要将数据后移;
-
跳表对数据的插入相对比较友好,直接修改指针就行;
-
跳表需要注意多级索引的退化,需要在合适的时机修改或重构索引;
zset的应用场景
滑动窗口限流
如:生产上要对外部调用系统进行限流,每分钟只能有1000的调用量

使用命令:
-
zadd 接口名 时间戳 x
-
zcount 接口名 时间戳-1分钟 时间戳 需要定时清理数据
延迟队列
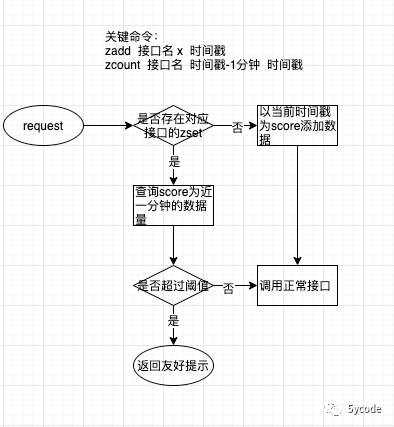
使用命令:
-
zadd key 时间戳 x
-
ZREMRANGEBYSCORE key 时间戳 时间戳+100毫秒 (需要注意一致性)
排行榜
-
zadd ranking_list 1 a 初始化
-
ZINCRBY ranking_list 1 a 浏览量+1
-
ZREVRANGE ranking_list 0 9 按score从大到小取10条

文章评论